0102030405
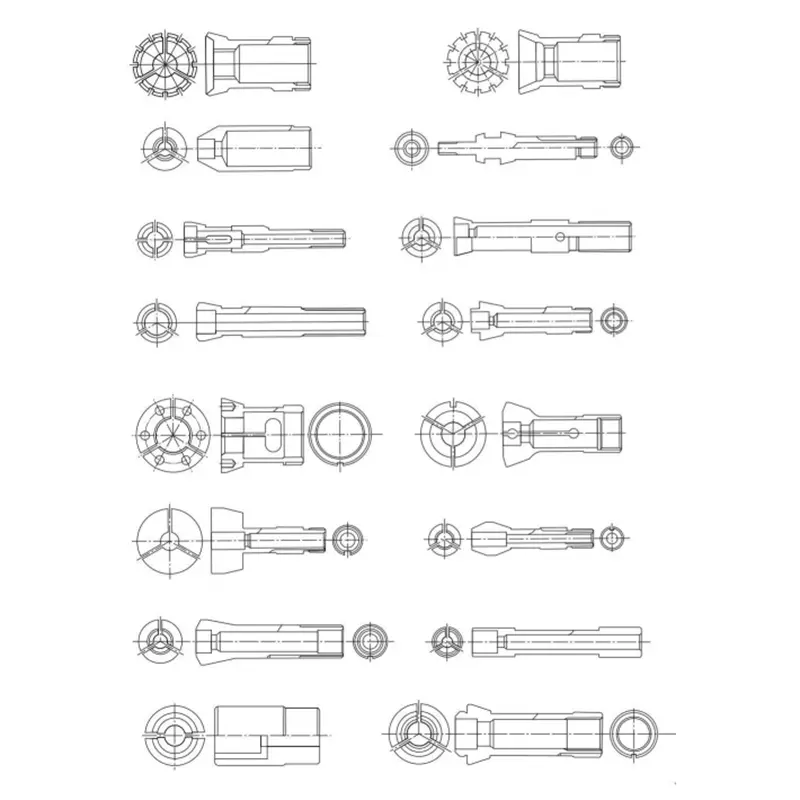
NGT & NK Series Rubber-Flex Collets
NGT series Parameters
 |
Rubber-flex collets NGT60 | |||||||
| type | D mm | L mm | W Unilateral angle | Clamping dia | Smooth | Radial groove | Serrated | |
| NGT60S | 59 | 32 | 30 | 4-32 | 4-32 | -- | -- | |
| NGT60N | 59 | 32 | 30 | 4-32 | -- | 8-11 | 12-30 | |
| Rubber-flex collets NGT105 | ||||||||
| type | D mm | L mm | W Unilateral angle | Clamping dia | Smooth | Radial groove | Serrated | |
| NGT105S | 104 | 42 | 30 | 6-42 | 15-72 | -- | -- | |
| NGT105N | 104 | 42 | 30 | 6-42 | -- | 8-11 | 12-42 | |
| Rubber-flex collets NGT145 | ||||||||
| type | D mm | L mm | W Unilateral angle | Clamping dia | Smooth | Radial groove | Serrated | |
| NGT145S | 145.7 | 47 | 16 | 25-120 | 25-120 | -- | -- | |
| NGT145N | 145.7 | 47 | 16 | 25-120 | -- | 8-11 | 12-52 | |
NK series Parameters
 |
Rubber-flex collets NK60 | |||||||
| type | D mm | L mm | W Unilateral angle | Clamping dia | Smooth | Radial groove | Serrated | |
| NK60S | 59 | 30 | 15 | 6-30 | 6-30 | -- | -- | |
| NK60N | 59 | 30 | 15 | 8-30 | -- | 8-11 | 12-30 | |
| Rubber-flex collets NK105 | ||||||||
| type | D mm | L mm | W Unilateral angle | Clamping dia | Smooth | Radial groove | Serrated | |
| NK105S | 104 | 40 | 15 | 6-42 | 6-42 | -- | -- | |
| NK105N | 104 | 40 | 15 | 6-42 | -- | 8-11 | 12-42 | |
What is a collet?
Collets are a type of chuck used to form a collar around an object and to clamp onto the object when tightened firmly. They’re mainly used within the industry to secure cutting tools and workpieces at high speeds and pressures.
Primarily, collets can be divided into two categories; external and internal collets.
● External collets – an external collet is, in essence, a sleeve, usually with a cylindrical internal surface and a conical external surface. External collets are the most commonly used type of collet. They hold the external surface of the tool or workpiece that’s being clamped such as a drill bit shank.
● Internal collets – an internal collet is presented in the form of a truncated cone, which has been drilled and threaded along the centreline. They expand inside the desired objects, securing them in place or holding two separate items, such as telescoping tubes, together. They are most often used to hold workpieces securely from the inside while the surface of the workpiece is machined on the outside.
Where are collets used?
While metalworking utilises the broadest range of collet varieties, collets are used in a surprising number of applications:
Woodworking
In woodworking, collets are used in various handheld and machine-operated rotating tools, from drill presses to routers. Furthermore, collets are also used to secure larger woodworking pieces during machining. Collets are favoured in woodworking applications as they are hardwearing and ideal for performing repetitive tasks.
Metalworking
Collets have a variety of applications in the metalworking industry. Their ability to secure small-diameter precision parts operating at very high speeds makes them especially suited to this type of work. Equally, their fast setup and release times make them ideal for use with multiple tools of a similar size.
Craft hobbies
Collets aren’t just used in industrial workholding. Hobbyist, artists, and craftspeople use tiny collets to secure interchangeable parts within handheld tools such as craft knives, drills, and files.
Watchmaking
Another use for tiny collets is in watchmaking, where watchmakers use collets that are sized in 0.1mm increments to secure the delicate workpieces to their lathes.
Combustion engines
Collets are used within combustion engines to regulate engine valves. Also known as valve locks, keepers, or clips, the collet attaches to the valve through the spring retainer and sits between the valve spring and the valve.
Semiconductors
Collets are used in the semiconductor industry to pick up a die from a wafer after a die-cutting process.